Understanding CORS in Web Development
- April 3, 2023
- Reading time . 2 min
- Author: Yuniel Acosta
Understanding CORS
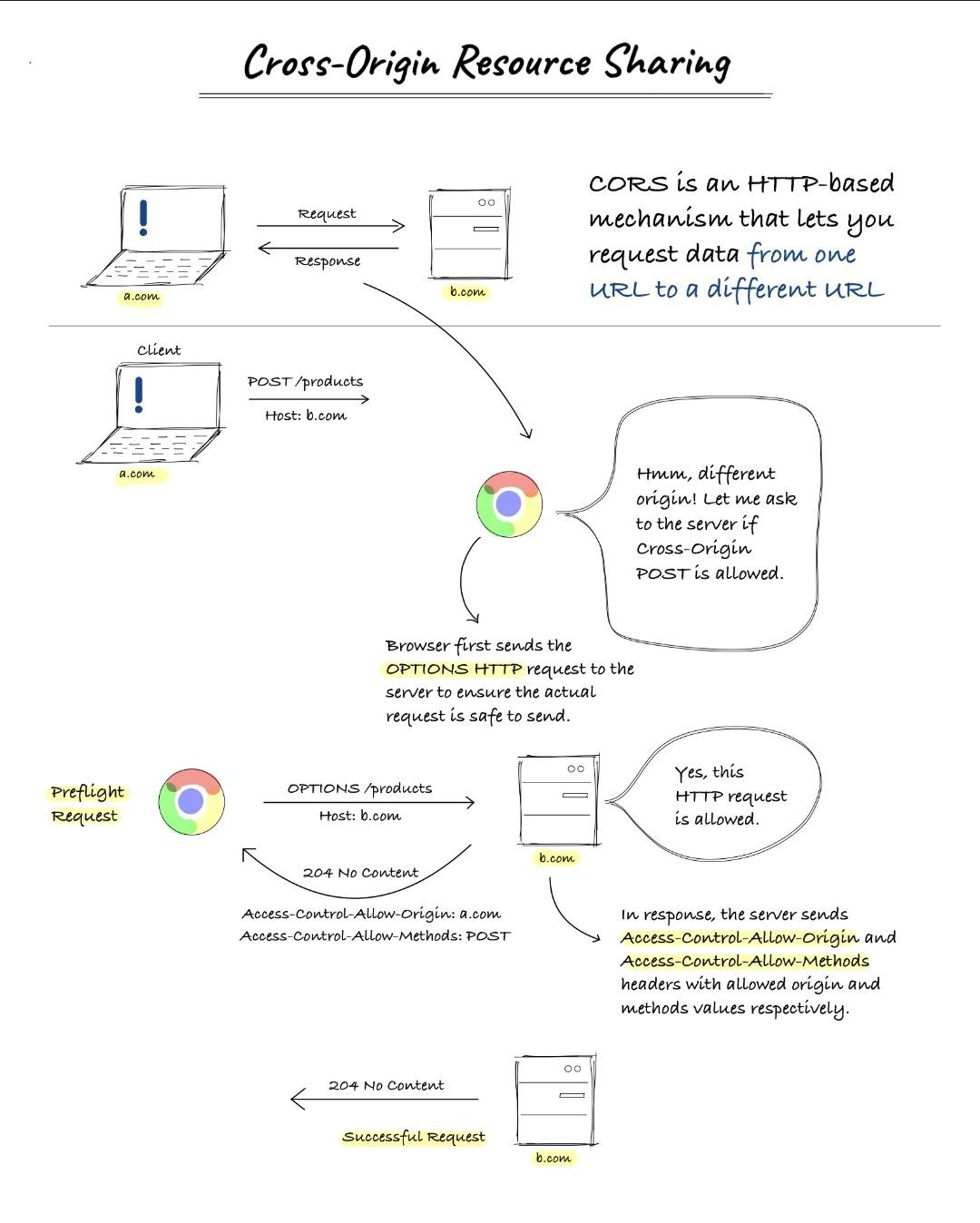
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a mechanism that allows a web page to make XMLHttpRequests to another domain. In other words, it is a security feature built into web browsers to prevent malicious websites from making requests to other websites on behalf of a user.
What is CORS?
CORS is a security feature built into web browsers that prevents malicious websites from making requests to other websites on behalf of a user. It is a mechanism that allows a web page to make XMLHttpRequests to another domain, which is normally prohibited by the same-origin policy.
Why is CORS important?
CORS is important because it allows websites to share resources with other domains, which is essential for building modern web applications. Without CORS, web pages would be limited to only making requests to the same domain, which would severely limit the functionality of the web.
How does CORS work?
When a web page makes a request to another domain, the browser will first send a preflight request to the server to determine whether the request is safe to make. If the server approves the preflight request, the browser will then make the actual request to the server and return the response to the web page.
Conclusion
CORS is an important security feature built into web browsers that allows websites to share resources with other domains. Without CORS, the functionality of the web would be severely limited. Understanding how CORS works is essential for building modern web applications that require cross-domain requests.